FORMAÇÃO DOS SUBSTANTIVOS
Os substantivos são usados para identificar ou dar nome às pessoas, coisas e qualidades que nos circundam.
Exemplos:
student, man, house, sky, Monday, France, hope, information.
Substantivos com sufixos que formam algumas profissões:
• R
Exemplos:
baker, builder, designer , manager, speaker, teacher
• ER
Exemplos:
engineer, footballer, gardener, lawyer, photographer, trumpeter, butcher, carpenter, grocer, plumber, usher
• OR
Exemplos:
actor, author, director, doctor, editor, professor, solicitor, surveyor, tailor
• IST
Exemplos:
cellist, pianist, violinist, geologist, physicist, economist, scientist, chemist, artist
• IAN
Exemplos:
mathematician, musician, politician, statistician, historian, librarian, technician
• ANT
Exemplos:
accountant, assistant, attendant, consultant, informant, inhabitant
• ENT
Exemplos:
resident, superintendent
Alguns sufixos formam substantivos abstratos:
• TION
Exemplos:
information, situation, solution, de nition, promotion
• SION
Exemplos:
explosion, persuasion, invasion, conclusion, decision, conversion, recession
• MENT
Exemplos:
amusement, judgment, excitement, argument, statement,
arrangement
• NESS
Exemplos:
sadness, readiness, usefulness, redness, business
• ANCE – ENCE – ANCY – ENCY
Exemplos:
independence, attendance, accountancy, eficiency, nuisance, emergency, conscience
• ABILITY – IBILITY
Exemplos:
probability, respectability, possibility, responsibility
• ISM
Exemplos:
classicism, communism, realism, liberalism, socialism, romanticism
Outros sufixos que também formam substantivos.
• AL
Exemplos:
arrival, committal, denial, dismissal, proposal, refusal,
withdrawal
• DOM
Exemplos:
kingdom, wisdom, random, condom
• HOOD
Exemplos:
likelihood, neighborhood, childhood, fairhood
• TH
Exemplos:
breadth, depth, length, width
GENDER OF NOUNS – GÊNERO DOS SUBSTANTIVOS
Em alguns casos, o feminino em inglês é formado a partir da adição do sufixo -ESS ao substantivo masculino.

Em alguns casos, há mudanças na ortografia.

Alguns substantivos masculinos apresentam formas irregulares de feminino.


Alguns substantivos apresentam apenas uma forma, tanto para o masculino quanto para o feminino.

Para distinguir o gênero dos substantivos que designam a maioria das espécies de animais, utilizam-se as formas male (macho) e female (fêmea).

THE PLURAL OF NOUNS – PLURAL DOS SUBSTANTIVOS
Como regra geral, o plural em inglês é formado a partir da adição de -S.


Substantivos terminados em –O com plural –ES

Terminados em –O com plural –S

Substantivos terminados em –Y, precedidos de consoante, perdem o -Y e acrescenta-se -IES para formar o plural.

Substantivos terminados em –Y, precedidos de vogal, acrescenta-se -S para formar o plural.

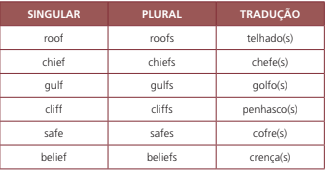
Alguns substantivos terminados em -F ou -FE perdem o -F ou o -FE e acrescenta-se -VES para formar o plural.

Nota:
Os substantivos dwarf (anão), wharf (cais), hoof (casco), handkerchief (lenço) e scarf (cachecol) podem formar o plural tanto pelo acréscimo de –VES, como acrescentando apenas –S (regra geral).
Exemplos:
dwarf- dwarves/dwarfs
wharf- wharves/wharfs
hoof- hooves/hoofs
handkerchief- handkerchieves/handkerchiefs
scarf- scarves/scarfs
Os demais substantivos terminados em -F, -FE ou -FF seguem a regra geral para formar plural, acrescentando apenas -S.
Alguns substantivos têm formas irregulares de plural.

Nos compostos separados por hífen, o componente substantivo é que recebe o sufixo de plural.

Substantivos de origem latina ou grega formam o plural das seguintes formas:
• Terminados em -US

• Terminados em -A

• Terminados em -UM, -ON

• Terminados em -EX, -IX

• Terminados em -IS

Substantivos incontáveis apresentam apenas forma de singular, logo concorda com o verbo no singular.

Exemplo:
The news is spread all over the world.
Substantivos que terminam em -S, mas estão no singular, concordam com o verbo no singular.


Exemplo:
The ethics is important in the world business.
Alguns substantivos são tipicamente utilizados apenas no plural, concordando com o verbo no plural.

Exemplo:
The pants are in the laundry.
Nota:
A palavra “people” só vai para o plural com –S quando se referir a povo(s).
Exemplo:
The native peoples of Philippines and their problems.
ADJECTIVES – ADJETIVOS
Os adjetivos em inglês são usados geralmente antes dos substantivos.
Exemplo:
wrong place, big house, small room, nice girl, tall man, thin boys, black cars
Alguns dos principais sufixos que formam adjetivos:
• Y
Exemplos:
healthy, cloudy, hungry, dirty, easy, funny, noisy, lucky
• LY
Exemplos:
brotherly, cowardly, fatherly, leisurely, friendly, monthly, lively
• LIKE
Exemplos:
businesslike, childlike, godlike, lifelike, workmanlike
• ISH
Exemplos:
childish, Spanish, foolish, reddish, Danish, snobbish
• FUL
Exemplos:
beautiful, shameful, careful, skillful, doubtful, useful, wonderful, harmful, hopeful
• LESS
Exemplos:
aimless, meaningless, careless, pointless, useless, hopeless, lifeless
• ABLE
Exemplos:
acceptable, considerable, eatable, readable, recognizable, respectable, believable
• IVE
Exemplos:
administrative, explosive, intensive, possessive, destructive, progressive
• ING
Exemplos:
daring, shocking, exciting, charming, boring, understanding
• ED
Exemplos:
disappointed, embarrassed, worried, satis ed, fascinated, reserved
Prefixos mais comuns:






